Oil & Gas
Drones Use in the Oil & Gas Industry
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have become integral to the oil and gas industry, providing a safe, efficient, and cost-effective solution for a variety of tasks. From inspection and monitoring to emergency response and environmental compliance, drones are transforming how the industry operates. Here’s a detailed overview of how drones are used in the oil and gas sector, the technologies involved, and the benefits they offer.
Key Applications of Drones in Oil & Gas
-
Inspection and Maintenance:
- Pipeline Inspections: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal sensors can inspect pipelines for leaks, corrosion, and structural integrity without the need for manual checks.
- Offshore Platform Inspections: Conduct detailed inspections of offshore rigs and platforms, including hard-to-reach areas such as flare stacks, reducing the need for risky manual inspections.
- Storage Tank Inspections: Inspect the condition of storage tanks, checking for signs of wear, leaks, and corrosion.
-
Monitoring and Surveillance:
- Site Surveillance: Provide real-time surveillance of oil and gas sites to enhance security and detect unauthorized activities or intrusions.
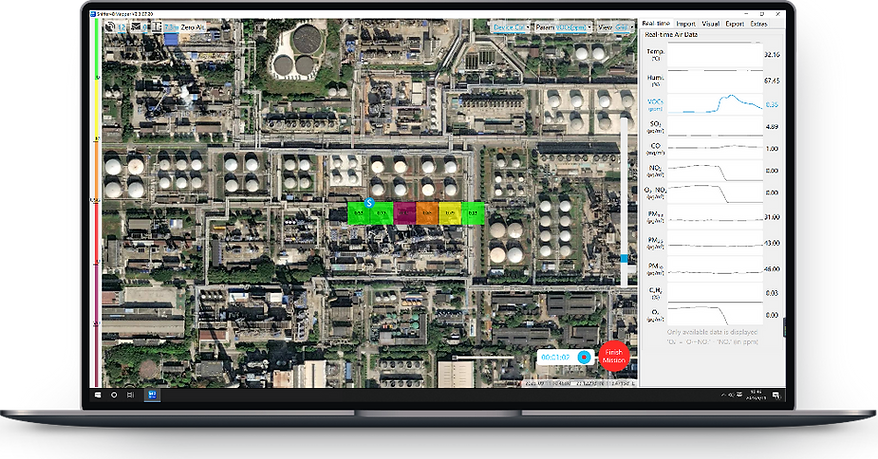
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitor environmental conditions around oil and gas facilities, including air quality, water quality, and vegetation health.
- Wildlife Monitoring: Track and monitor wildlife in and around oil and gas operations to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
-
Emergency Response:
- Incident Assessment: Quickly assess the situation during emergencies such as spills, fires, or explosions, providing real-time data to first responders.
- Search and Rescue: Assist in search and rescue operations by providing aerial views and thermal imaging to locate individuals in hazardous conditions.
-
Mapping and Surveying:
- Site Mapping: Create detailed maps and 3D models of oil and gas sites for planning and analysis.
- Topographic Surveys: Conduct topographic surveys to support construction and maintenance activities.
-
Asset Management:
- Inventory Management: Monitor and manage inventory levels of equipment and materials stored at oil and gas sites.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: Continuously monitor the condition of infrastructure, including roads, pipelines, and facilities.
Technologies Involved
-
Cameras and Sensors:
- High-Resolution Cameras: Capture detailed images and videos for visual inspections.
- Thermal Cameras: Detect temperature anomalies that indicate leaks, overheating equipment, or insulation failures.
- Gas Detection Sensors: Measure concentrations of gases such as methane, CO2, and NOx to detect leaks and emissions.
- LiDAR Sensors: Generate precise 3D models of terrain and infrastructure, useful for mapping and surveying.
-
Data Processing and Analysis:
- Image Processing Software: Stitch images together to create orthomosaics and detailed maps.
- 3D Modeling Tools: Create accurate 3D models from LiDAR and photogrammetric data.
- AI and Machine Learning: Automate the detection of defects, leaks, and other anomalies in the data collected by drones.
Benefits of Using Drones in Oil & Gas
-
Safety:
- Reduced Risk: Minimize the need for workers to perform dangerous tasks such as climbing flare stacks or inspecting offshore platforms.
- Remote Inspections: Conduct inspections remotely, reducing the risk of accidents and exposure to hazardous environments.
-
Efficiency:
- Time Savings: Drones can quickly cover large areas and difficult-to-reach locations, significantly reducing inspection and survey times.
- Real-Time Data: Provide immediate access to high-quality data for faster decision-making and response.
-
Cost-Effectiveness:
- Lower Operational Costs: Reduce the need for expensive equipment such as scaffolding, cranes, and helicopters.
- Preventive Maintenance: Early detection of issues helps prevent costly repairs and downtime.
-
Accuracy:
- High-Resolution Data: Capture detailed and accurate images and measurements for precise analysis.
- Consistent Monitoring: Automated and repeatable flights ensure consistent data collection over time.
-
Environmental Compliance:
- Leak Detection: Quickly identify and address leaks and emissions to minimize environmental impact.
- Regulatory Reporting: Provide accurate and comprehensive data to meet regulatory requirements for environmental monitoring.
Featured collection


DJI - Mavic 3 Thermal - 1 year Shield Protection Basic
Sale price$5,498.00


DJI Mavic 3 Thermal - 2 Years Shield Protection Basic
Sale price$5,748.00


Qysea - Fifish V6 Expert - M100A
Sale price$3,999.00


Qysea - Fifish V6 Expert - M200A
Sale price$4,299.00


DJI Mavic 3 Thermal - 1 Year Shield Protection Plus
Sale price$5,998.00
Save 33%

DJI - Matrice 30T with Shield Basic (No Batteries)
Sale price$8,979.00
Regular price$13,341.00


Qysea - Fifish V6 Expert - M200
Sale price$3,599.00


Autel Robotics - EVO II Dual 640T Enterprise Bundle V3
Sale price$5,299.00


Parrot - Anafi USA with Skycontroller 4
Sale price$7,000.00
Save 33%

DJI - Matrice 30T with Shield Plus (No Batteries)
Sale price$9,456.00
Regular price$14,042.00


Sniffer4D Mini2
Sale priceFrom $8,723.00


Autel - EVO Max 4N
Sale price$12,599.00

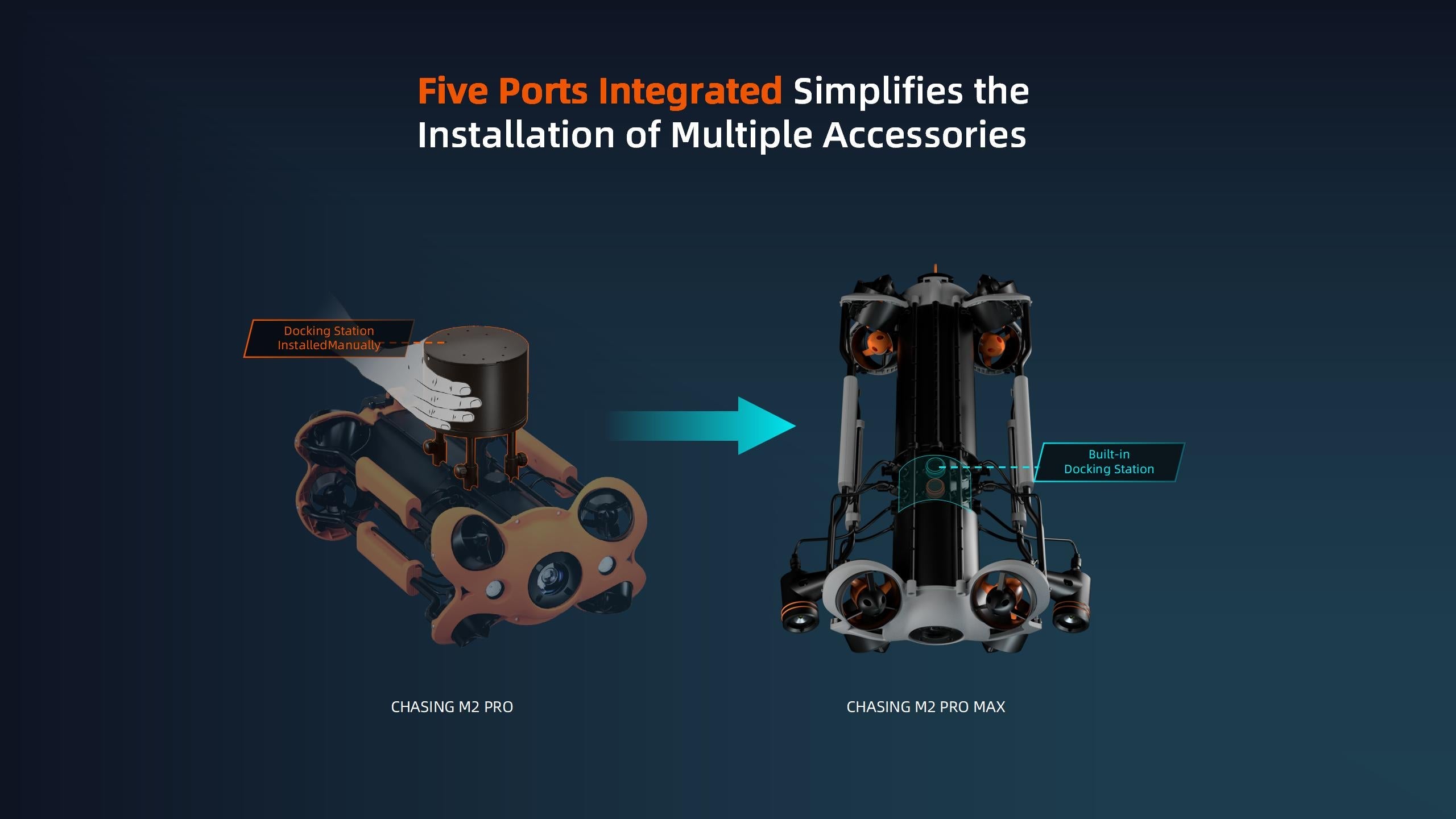
Chasing - M2 Pro Max Advanced Set (200M) ROV
Sale price$6,999.00


Anzu Robotics - Raptor T (Thermal)
Sale price$7,699.00


Teledyne FLIR SIRAS Combo
Sale price$9,695.00


Qysea - Fifish V6 Expert - MP200
Sale price$6,199.00


Autel Robotics EVO II V3 640T Gimbal Camera
Sale price$3,359.00


DJI - Zenmuse H20
Sale price$4,364.00


Autel Robotics - EVO Lite 640T Enterprise Standard Package
Sale price$3,359.00


Autel Robotics - EVO Lite 640T Enterprise 7.9" RC Premium Package
Sale price$3,879.00


Autel Robotics - EVO Lite 640T Enterprise Premium Package
Sale price$3,879.00


DJI - Matrice 350 RTK With H30T Hybrid Camera with Batteries & Charger
Sale priceFrom $21,189.00


DJI - Matrice 350 RTK With H30T Hybrid Camera
Sale priceFrom $18,589.00


DJI Matrice 3TD
Sale priceFrom $6,050.00


DJI - Dock 2 for Matrice 3D and 3TD
Sale price$9,000.00
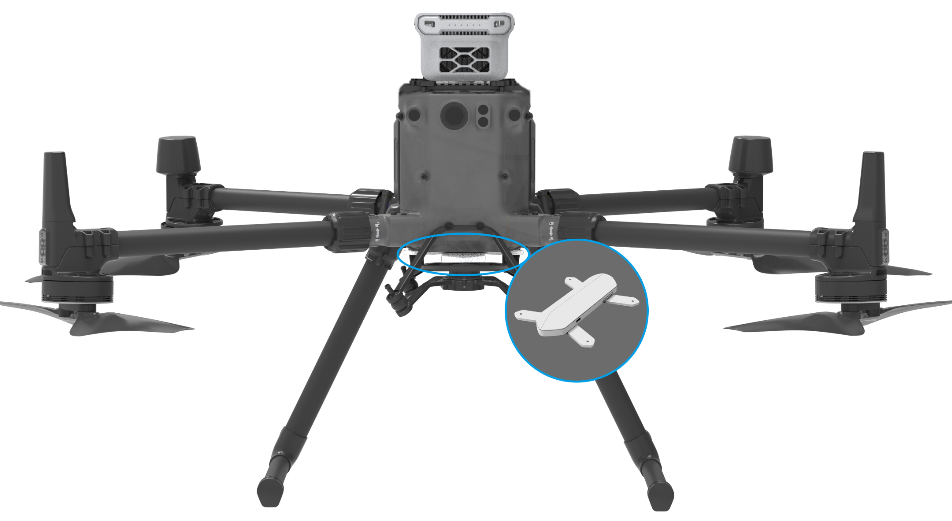

Nuclear Radiation Sensing Module - Optional Module
Sale price$5,700.00


DJI - Zenmuse H30 Quad-Sensor Camera (Wide, Zoom, Rangefinder, NIR Aux)
Sale priceFrom $3,520.00


DJI - Zenmuse H30T Infrared Density Filter
Sale price$169.00
Save 84%

DJI - FLIR Zenmuse XTR640 Radiometric 13mm 30hz - USED
Sale price$1,250.00
Regular price$8,000.00


Autel - Alpha L35T Bundle
Sale price$19,289.00


Chasing - M2 Pro Max Professional Set (200M) ROV
Sale price$11,999.00


Qysea - Fifish V6 Expert - EP300
Sale price$12,999.00


Parrot - Anafi Ai Drone
Sale price$4,500.00
Save 31%


DJI - Matrice 30 with Shield Plus (No Batteries)
Sale price$6,884.00
Regular price$9,942.00


Autel Robotics - Evo II Dual 640T RTK Rugged Bundle V3
Sale price$5,799.00
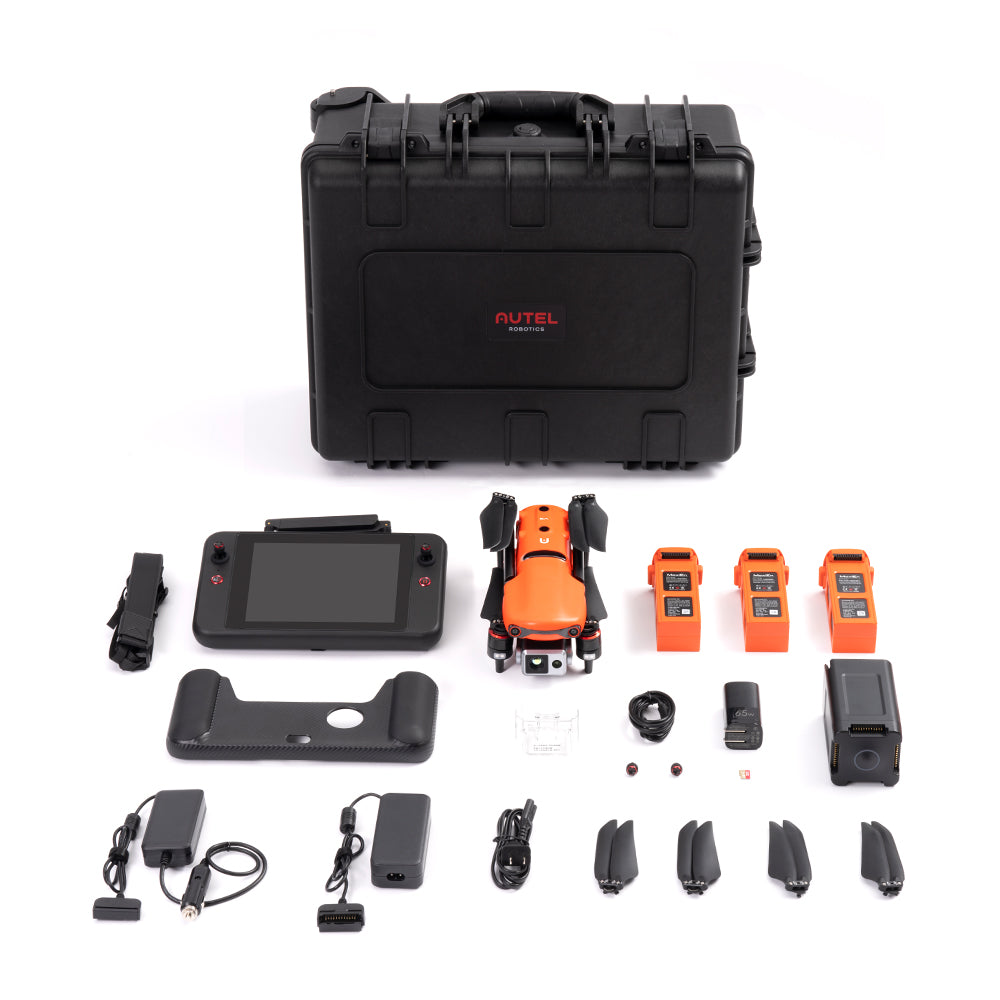


Autel Robotics - Evo II Dual 640T Rugged Bundle V3
Sale price$4,799.00